RAIN RFID is a key technology for organisations to automatically capture highly accurate and reliable information about individual items or assets within their operations and supply chain. Information about the product’s identity is stored in the IC and communicated to readers when interrogated.
Memory banks of RFID tags are quite resilient, but like every other memory, they can be damaged, and data integrity can be compromised. Companies apply RFID tags to products and parts. Later, during processing, companies often can’t fully control the handling of the item over the products life cycle. While almost everyone understands not to drop a phone or computer, RFID tags are regularly exposed to shock and other forces such as heat and humidity.
RFID tags are designed to provide a unique identifier for individual items, and the technology is inherently reliable for this purpose. Many industries have the desire to store additional business data on the IC, and while this is possible, it is recommended to use enterprise systems to hold this information. A best practice is only to use the unique identifier as a pointer to look up the data in your enterprise-grade IT systems.
Physical Damage
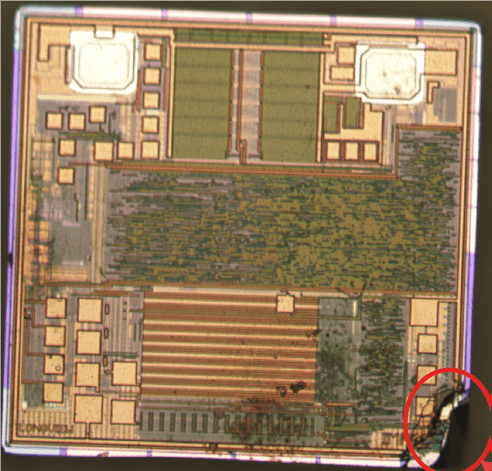
You can identify physical damage to the IC through microscopic analysis of the die. Physical damage can show in many different ways; in the best case, the IC may no longer be functional. In other occasions, the device may show unexpected behaviours or provide inconsistent data.
Impact of Heat
Exposure to heat can reduce the ability of single or multiple memory cells to retain charge over time. Damaged ICs may function correctly right after encoding, but bits of memory may be corrupted, flip and impact the consistency of the data stored over time. While under normal conditions, memory cells should retain their charge for an estimated 10-50 years, heat can reduce this to a few years, days or hours.
Data Integrity features in modern IC generations
Enterprise IT systems have safeguards in place to ensure data integrity, system availability and backups for disaster recovery. In the last years, RFID IC manufacturers have recognised the importance of data integrity and developed features to minimise the risk of corrupted data entering production IT systems.
Modern IC generations self-test and diagnose the integrity of data before they transmit information to the reader requesting information. Impinj calls this feature Integra, and it was first released with Monza R6. The equivalent feature from NXP is called Memory Safeguard and is available with UCode8.
Solutions for older IC generations
For various reasons, you may need to use older IC generations in business-critical processes such as automotive or healthcare. In those cases, we strongly recommend analysing the inherent risk from memory failures on your operations and regulatory traceability obligations. Integrating error detection or correction codes into your encoding scheme may increase the resilience of the data captured and improve your overall data quality. This strategy will give you the confidence that you meet regulatory requirements and minimise the risk of errors from inconsistent data.
Physical damage and heat can impact the integrity of RFID memory cells.